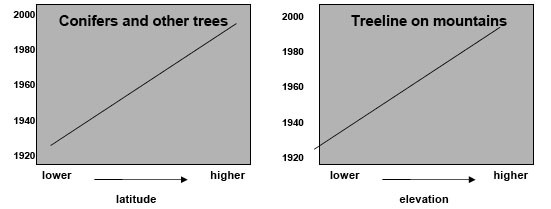
Plant communities across the globe are responding as predicted. Describe the general shifts in distribution shown in the charts below.
Will future climate change be too rapid for plants to adapt to existing locations or migrate to new habitats, meeting new competitors and pests? Plants are rooted in place. Being stationary organisms makes plants susceptible to rapid climate change because they can migrate only when dispersing seeds for the next generation. Barriers to migration may prevent some plants and animals from moving to new habitats. List three man-made obstacles and three natural barriers.
The average temperature across the world will increase with global warming, but the effects of climate change will vary from region to region. Consider each situation below and predict how plants will respond to climate changes in each area.
| Florida Keys, Florida | Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, Alaska |
|---|---|
| The conditions: Along
with global warming, |
The conditions:
Ground temperatures are |
| The plant community: coastal pine forests | The plant community:
forbs and lichens of the |
| Predicted plant response: | Predicted plant response: |
| Rocky Mountain National Park, Colorado | A natural area in your region |
| The conditions:
Warmer temperatures at |
The conditions:
What are predicted climate |
| The plant community:
alpine flower |
The plant community:
What plants are typical |
| Predicted plant response: | Predicted plant
response: Will particular |
Why are some plant species more vulnerable to change than others?
How will changing conditions affect our food crops?