aristate -
with an awn
aristulate
- diminutive of aristate
auricle -
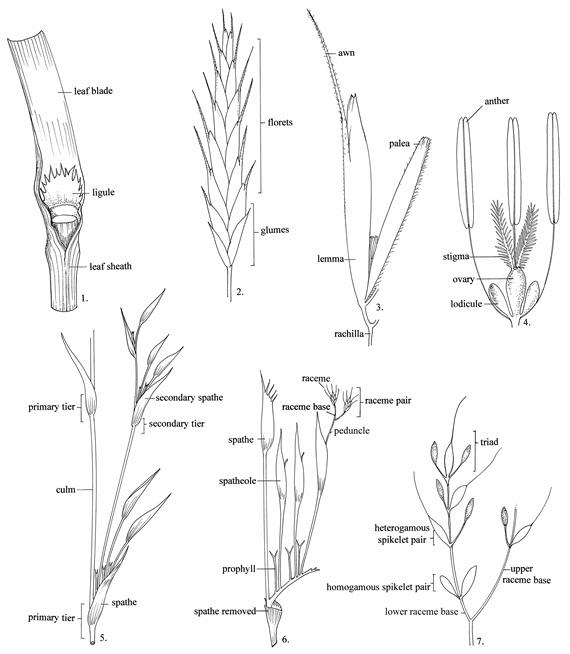
an earlike lobe or appendage at the junction of leaf sheath and blade
auriculate
- with an auricle
awn - a
bristle arising from a spikelet part
callus - a hard projection at the base of a
floret, spikelet, or inflorescence
segment, indicating a disarticulation point
caryopsis - a specialized dry fruit characteristic of grasses, in
which the seed and ovary wall have become united
collar -
pale or purplish zone at the junction of leaf sheath and blade
column -
the lower twisted portion of a geniculate awn, or the part below the awn
branching-point in Aristideae
compound - referring to inflorescences made up of a number of
small constituent inflorescences (as in some Andropogoneae),
or a raceme with some secondary branching
culm - the
flowering stem of a grass plant
culm sheath
(bamboos) - modified, often non-photosynthetic, culm leaf with an expanded sheath
and much reduced blade, usually deciduous as the culm matures
diffuse (bamboos)
- culms arising singly from long slender rhizomes.
extravaginal - branching in which the young shoot breaks through the
base of the leaf sheath
floret - the individual unit of a spikelet, comprising a lemma
and palea with enclosed reproductive organs
glume - one of a pair of empty scales at the base of a grass
spikelet
heterogamous spikelets - the paired spikelets found in most Andropogoneae, where one spikelet of the pair is sessile and
produces a caryopsis, and the other spikelet is pedicelled, of different form,
and staminate or sterile
hilum - the
scar on the caryopsis marking the site of the attachment of the pericarp and
testa, found on the opposite side from the embryo
homogamous spikelets - in Andropogoneae the
paired spikelets sometimes present at the base of the raceme, of similar
appearance and not producing any caryopses, often resembling the pedicelled
spikelets or assuming a protective involucral function
intravaginal - branching in which the young shoot grows up inside
the leaf sheath, emerging at the sheath mouth
iterauctant
(bamboos) - inflorescence with
pseudospikelets with glumes subtending axillary buds capable of partial or extensive
spikelet ramification
leaf blade - the distal
expanded part of a grass leaf
leaf sheath
- the basal part of the grass leaf which normally encloses a culm internode
lemma - the
lower of the two bracts enclosing the grass flower and together with the palea
comprising a floret
leptomorph
(bamboos) - rhizome monopodial, elongated, more slender than culms
ligule - a
membrane or line of hairs on the inner (adaxial) side of the junction of the
leaf sheath and leaf blade; bamboos sometimes have an external ligule on the
abaxial side of the junction
lodicule -
a small scale-like or fleshy structure at the base of the stamens in a grass
floret, usually 2 in each floret (often 3 or more in bamboos); they swell at
anthesis, causing the floret to gape open
oral setae
- marginal setae inserted at junction of leaf sheath and blade, on the auricles
when these are present
pachymorph
(bamboos) - rhizome sympodial, thicker than culms
palea - the upper and inner scale of the grass floret which
encloses the grass flower, usually 2-keeled
panicle -
in grasses, an inflorescence in which the primary axis bears branched secondary
axes with pedicellate spikelets
pedicel - in grasses, the stalk of a single
spikelet within an inflorescence
peduncle -
the stalk of a raceme or cluster of spikelets
pluricaespitose (bamboos) - culms arising in a series of clusters along a long slender
rhizome
prophyll -
in grasses, a 2-keeled, hyaline, modified leaf, placed within a leaf sheath on
the adaxial side of a branch
pseudopetiole
- the narrow basal portion of some leaf blades, resembling a petiole
pseudospikelet (bamboos) - spikelet
in which the outer glumes or bracts
subtend axillary buds which can develop to form lateral spikelets or branches
raceme - in
grasses, an unbranched axis bearing spikelets; racemes may be solitary, digitate,
or scattered
raceme base
- short stalk beneath the individual racemes of a pair in some Andropogoneae
raceme pair - pairs of racemes supported by
spatheoles in the compound panicles of
some Andropogoneae
rachilla -
the central axis of the spikelet which bears the florets
rachilla extension - a prolongation of the rachilla beyond the uppermost
(or single) floret
rachis -
the axis of a raceme
secondary spathe - spathe supporting a second tier of branching within the compound
panicle of some Andropogoneae
semelauctant
(bamboos) - inflorescence with glumes not subtending viable buds or branches
sinus - the
space between two projecting lobes or teeth
spathate - with spathes
spathe - a bract or modified bladeless leaf subtending the
inflorescence or part of it
spatheole -
the uppermost spathe supporting the racemes within the compound inflorescence
of some Andropogoneae
spikelet -
the basic unit of a grass inflorescence; usually composed of two glumes and one
or more florets on a rachilla
spikelet pair - the arrangement of one sessile and one pedicelled spikelet
arising from the same node characteristic of the Andropogoneae
tiller - a
leafy non-flowering shoot
triad - a
group of three spikelets borne together
unicaespitose
(bamboos) - culms all arising in a single clump from pachymorph rhizomes